In a remarkable twist of fate, Abraham A, a former paramilitary soldier hailing from Kerala, found himself at the forefront of a fascinating discovery in 2020 – a new species of subterranean fish known as the Pathala Eel Loach. This remarkable find sheds light on the mysteries of underground ecosystems and showcases the power of citizen science in advancing our understanding of the natural world.
International
Andhra Pradesh Unveils Multi-Pronged Strategy to Boost Domestic Seafood Market
Despite its extensive coastline spanning nearly 1,000 kilometers and the opportunity for fishing within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) up to 200 nautical miles, Andhra Pradesh faces a significant challenge in establishing a reliable and robust domestic market for its abundant seafood products. In response, the state government has devised a comprehensive marketing strategy that encompasses seafood festivals and the establishment of branded retail outlets, aiming to transform the dynamics of the seafood industry.
According to VV Rao, Joint Director of the Fisheries Department, the absence of a strong domestic market has left aquaculture entrepreneurs, particularly those involved in shrimp farming, at the mercy of a “buyer’s market.” To tackle this issue, the Fisheries Department is partnering with Bhoomi Organics to organize seafood festivals. These festivals are envisioned to promote seafood consumption, stimulate demand, and connect entrepreneurs with consumers.
Rao emphasized the abundance of marine fish, natural water bodies, and shrimp production in Andhra Pradesh. The state boasts 5.75 lakh tonnes of marine fish, 4.75 lakh hectares of natural water bodies (including reservoirs, lakes, and ponds), and up to 20 lakh tonnes of cultured shrimp, resulting in an annual production of 52 lakh tonnes of fish, shrimp, and aquaculture products from various sources.
Despite being a major exporter of shrimp, with approximately 15 lakh tonnes shipped abroad, Andhra Pradesh consumes only three to four lakh tonnes of shrimp locally. This export-oriented approach raises concerns about the sustainability and profitability of aquaculture entrepreneurs within the state. To counter this trend, the government seeks to boost local consumption of seafood.
With mutton prices soaring to ₹1,000 per kilogram and concerns surrounding poultry, Rao sees seafood as a natural, nutritious, and affordable alternative. He highlighted the health benefits of seafood, which is rich in nutrients and available for as low as ₹50.
Raghuram from Bhoomi Organics stressed that the term “organic food” extends beyond groceries and plant-based products to include anything free of chemicals. He argued that fish from the sea and natural water bodies qualify as organic, as they rely on a natural food chain, beginning with plankton and aquatic organisms.
He also raised concerns about hormones in chicken and milk, which he believes contribute to hormonal imbalances and health issues such as polycystic ovarian disease (PCOD).
Fisheries Commissioner K Kanna Babu reported that seafood festivals have already gained traction, with thousands of food enthusiasts relishing unlimited seafood buffets priced at ₹699 per head. These festivals have attracted substantial footfall, and plans are underway to host them in various locations across the state.
Additionally, the government is actively establishing “Fish Andhra” retail outlets under a hub-and-spoke model. Currently, three are operational, and 15 are under construction out of a total of 26 hubs. The goal is to increase the number of retail outlets from 2,000 to 4,000 by March next year. These outlets will offer online ordering options and provide seafood in live and packaged formats. Entrepreneurs can benefit from generous subsidy schemes, training, and guidance to set up their outlets.
Despite these endeavors, Commissioner Babu acknowledged that there is still much work to be done. While non-vegetarian cuisine enjoys immense popularity in Andhra Pradesh, the average seafood consumption per person per annum stands at less than 8 kilograms, signaling an untapped domestic market.
He also emphasized the importance of not leaving entrepreneurs at the mercy of international markets and the need to foster a thriving domestic seafood industry.
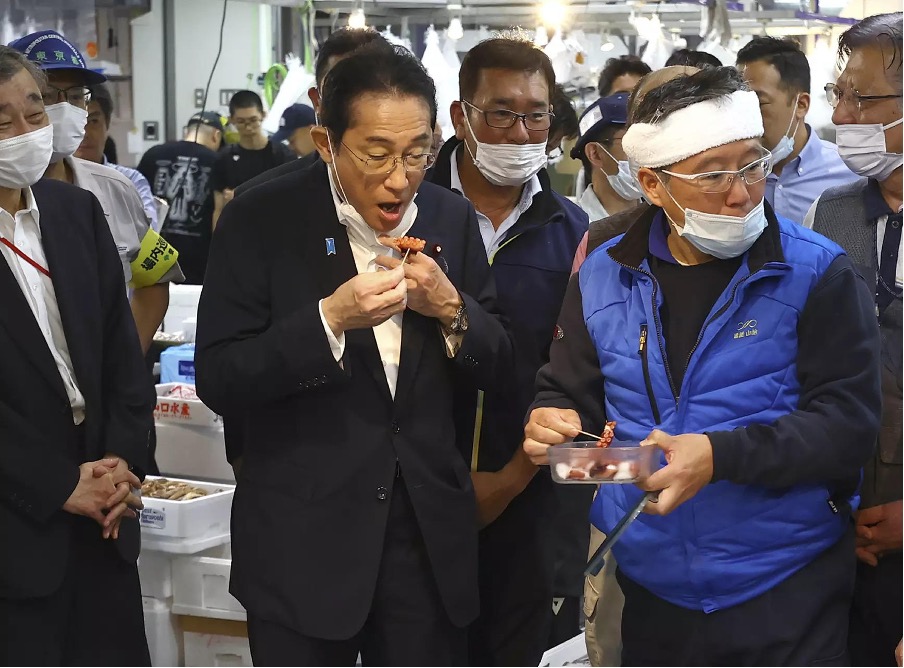
Japan’s Prime Minister Fumio Kishida made a visit to Tokyo’s Toyosu fish market, where he sampled seafood and spoke with workers to evaluate the repercussions of China’s ban on Japanese seafood. The ban was enacted in response to Japan’s release of treated radioactive wastewater from the damaged Fukushima Daiichi plant into the sea, a process that commenced last week and is expected to persist for decades. Prior to the water release, China had already increased scrutiny of Japanese fisheries products at customs, leading to significant delays and affecting seafood prices and sales, extending beyond Fukushima to regions like Hokkaido.
Japanese officials have urged domestic consumers to increase their consumption of scallops to support struggling exporters, while simultaneously seeking new export markets in Europe and the United States. Notably, all seawater and fish sampling data since the wastewater release have consistently remained well below established safety limits for radioactivity, according to both officials and the operator, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings.
In response to China’s seafood ban, Chief Cabinet Secretary Hirokazu Matsuno hinted at the possibility of taking the case to the World Trade Organization (WTO). Japan has previously raised concerns about China’s trade restrictions lacking scientific basis and intends to explore various options while emphasizing the importance of dialogue, as highlighted by Foreign Minister Yoshimasa Hayashi. The ban’s impact has also extended to tourism, with increased cancellations of Chinese group tourists and inquiries about food safety in Japan, prompting officials to assess the situation.
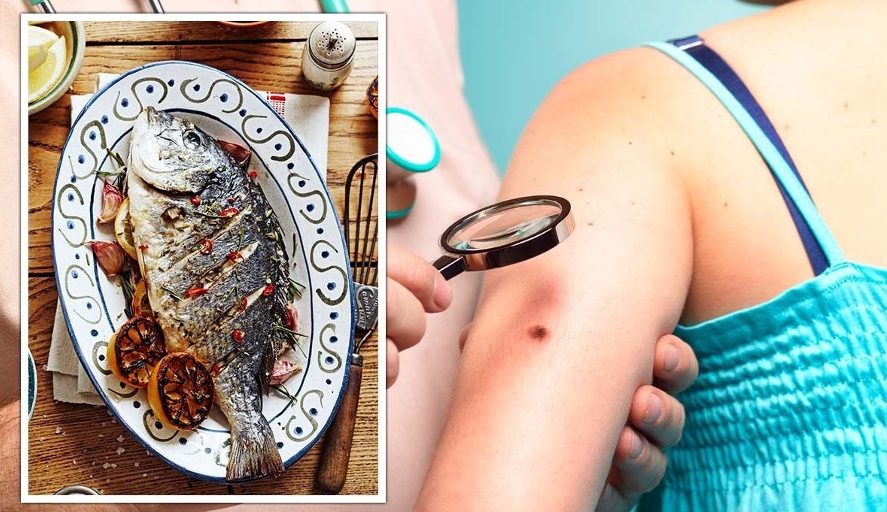
Study Reveals Surprising Link Between Fish Consumption and Skin Cancer Risk
A recent study conducted as part of the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study by Brown University has brought to light a startling revelation: consuming two portions of fish each week might be associated with an increased risk of developing skin cancer. The findings, published in the journal ‘Cancer Causes and Control,’ have garnered attention for their unexpected implications in the world of dietary recommendations and skin health.
Fish Intake and Skin Cancer Risk
The study, which involved an extensive examination of 491,367 adults in the United States, found a noteworthy connection between fish consumption and skin cancer risk. Specifically, individuals who consumed an average of 42.8 grams of fish per day (equivalent to approximately 300 grams per week) faced a 22 percent higher risk of malignant melanoma, a severe form of skin cancer, compared to those whose daily fish intake was a mere 3.2 grams.
Moreover, the study unveiled an intriguing correlation between increased fish consumption and the development of abnormal skin cells in the outer layer, referred to as stage 0 melanoma or melanoma in situ. This is a precursor to one of the most prevalent forms of skin cancer. While fish is often lauded for its nutritional benefits, including omega-3 fatty acids and essential vitamins, the study suggests that it may also harbor certain risks.
Dr. Eunyoung Cho, one of the study’s authors, raised concerns about potential contaminants in fish that could be contributing to the observed risks. These contaminants include polychlorinated biphenyls, dioxins, arsenic, and mercury, all of which can have detrimental health effects. While previous research on the link between fish intake and melanoma risk has been limited and inconsistent, this study brings attention to a previously unexplored aspect.
UV Radiation and Skin Cancer
Dr. Niti Raizada, Director of Medical Oncology and Hemato-Oncology at Fortis Hospitals in Bangalore, noted that while the exact cause of all melanomas is not clear, exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight remains a known risk factor. However, this new research introduces an intriguing twist to the narrative.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Cooking Methods
Dr. Hitesh R Singhavi, Consultant-Head and Neck Onco Surgery at Fortis Hospital Mulund, highlighted the potential impact of cooking methods on the nutritional value of fish. He explained that frying fish can significantly reduce its omega-3 fatty acid content, which is a primary source of its nutritional benefits. Thus, the daily consumption of fish may not necessarily provide the expected nutritional advantages, but this data is still considered inconclusive.
Expert Perspectives
Experts caution against jumping to conclusions and discontinuing fish intake altogether. Dr. Rinky Kapoor, a consultant dermatologist, cosmetic dermatologist, and dermato-surgeon at The Esthetic Clinics, emphasized that the study’s findings may not be directly applicable to individuals with pigmented skin, such as Indians and Asians, who have a long history of fish consumption without a notable increase in melanoma risk.
This study’s unexpected findings highlight the complexity of dietary recommendations and their potential impact on health. While fish consumption is associated with numerous benefits, including omega-3 fatty acids and essential vitamins, it may also carry unforeseen risks. As the scientific community continues to explore this connection, individuals are advised to maintain a balanced diet and consider the potential implications of their dietary choices on skin health.
Captain Fresh, a B2B fish and seafood startup, has successfully raised $20 million in an extended Series C funding round, with primary investments from SBI Investment and Evolvence Capital, both based in Japan. The round also saw continued support from existing investors including Accel, Matrix Partners India, Prosus Ventures, and Tiger Global, highlighting the startup’s growing appeal within the industry. The fresh injection of capital will be instrumental in realizing Captain Fresh’s global ambitions, as it sets its sights on expansion into European and US markets.
The company has already commenced discussions with potential partners in these regions as part of its strategic growth plan. To bolster its European expansion, Captain Fresh has appointed Basola Valles as CEO – Europe, who expressed the company’s commitment to introducing their tech-enabled sourcing capabilities to Europe. This initiative aims to streamline distribution processes, reduce turnaround times, invest in product innovation, and address growing demands for transparency and traceability.
Captain Fresh relies heavily on the Indian Ocean Region for its supply, with India accounting for a substantial 90% of its sourcing. In terms of demand, Europe, the US, and India each contribute roughly equal shares, with additional demand originating from South East Asia. The startup boasts an extensive product portfolio, offering over 100 varieties of fish and seafood, and serves clients in more than 30 countries globally. Its operational footprint spans across India, the US, Dubai, and Madrid.
Rohit Batra, Managing Partner at Evolvence India, commended Captain Fresh for successfully consolidating a previously fragmented and unorganized industry. He also praised the company for building a robust demand network, demonstrating impressive execution capabilities, and showcasing attractive unit economics.
Founded in 2019 by Utham Gowda, Captain Fresh has been on a mission to revolutionize India’s fish and seafood supply chain. Their innovative approach combines a digital commerce platform with a strong physical fulfillment layer, enabling retailers across various formats to access dependable, equitable, and transparent purchasing experiences
Captain Fresh has been steadily attracting investment interest, with a $50 million Series C round last March, co-led by existing investors Prosus Ventures and Tiger Global. In June 2021, it raised $12 million in a Series A round led by Accel Partners, with participation from Matrix Partners India, Ankur Capital, and Incubate Fund.
Sands Expo and Convention Centre in Singapore is set to host the 11th edition of Seafood Expo Asia from September 11 to 13, 2023. This year’s event promises to be the largest in its history, with over 350 exhibitors representing 40 countries participating in the three-day expo. Following a successful in-person event in 2022, Seafood Expo Asia is once again bringing its conference program and introducing the inaugural Seafood Excellence Asia Awards.
Organized by Diversified Communications, the expo will offer a comprehensive conference program covering a wide range of topics, including seafood consumption trends in Asia, supply chain sustainability, and innovation. The event will also feature special events such as an oyster challenge where talented chefs will compete head-to-head, a culinary demonstration by chef Flavio Morganti of Spain showcasing the best of Galicia’s coastal products, and various product tastings at the Tasty Kitchen.
One of the highlights of this year’s Seafood Expo Asia is the introduction of the Seafood Excellence Awards Asia. This expansion of the Seafood Excellence Awards program, previously featured at Seafood Expo Global and Seafood Expo North America, will have key buyers evaluating innovative products submitted for the awards competition. The winners in both the retail and hotel, restaurant, and catering (HORECA) categories will be announced on the second morning of the event, Tuesday, September 12.
Seafood Expo Asia continues to be a significant platform for the global seafood industry, fostering connections, and showcasing the latest trends and innovations in the sector. With its impressive lineup of exhibitors and diverse program, the expo is set to provide valuable insights and opportunities for seafood professionals and enthusiasts alike.
Japan’s plan to release more than a million tons of water from the Fukushima plant, starting on Thursday, has sparked concerns both domestically and internationally. While the move has been approved by the United Nations nuclear watchdog, it faces opposition from various quarters. Hong Kong’s leader expressed strong opposition to Japan’s decision, echoing concerns about potential risks to food safety. China has also lodged a formal complaint with the Japanese government, with a foreign ministry spokesperson branding the move “extremely selfish.”
Tokyo’s proposal involves discharging 1.32 million metric tonnes of treated radioactive water, a volume equivalent to that of 500 Olympic swimming pools, into the ocean gradually over a span of 30 years. This has raised apprehensions regarding the potential enduring impacts on the marine ecosystem and food chain.
Import Ban Details
Effective from Aug, 24th, Hong Kong’s import ban covers a range of aquatic products originating from specific Japanese regions. These regions include Tokyo, Fukushima, Chiba, Tochigi, Ibaraki, Gunma, Miyagi, Niigata, Nagano, and Saitama. The government has not specified a duration for the ban, indicating that its duration will depend on data and information received from Japan after the water discharge.
However, it’s important to note that seafood imports from 13 other Japanese regions will continue to be allowed. The ban encompasses various forms of aquatic products, such as live, frozen, refrigerated, and dried seafood, as well as sea salt and seaweed.
Impact on Trade
Hong Kong is a significant market for Japanese agricultural and fisheries exports, ranking as Japan’s second-largest market after mainland China. In the previous year, Hong Kong imported Japanese seafood worth 75.5 billion yen (approximately $519.54 million), according to Japanese data.
The measures taken by Hong Kong reflect global concerns surrounding Japan’s decision to release Fukushima’s treated radioactive water into the sea. As the situation unfolds, Hong Kong remains committed to safeguarding its citizens’ health and maintaining food safety standards in seafood imports from Japan.
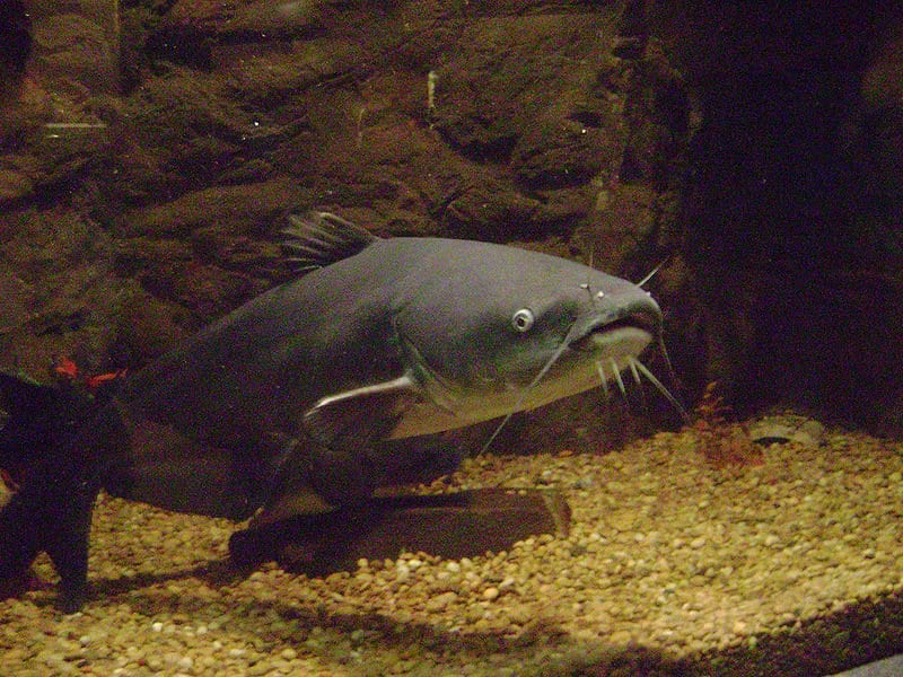
Innovative Solution: Alligator DNA Injected into Catfish to Boost Disease Resistance
In the United States, where catfish is a popular choice for consumption, fish farms produced approximately 307 million pounds of catfish for human consumption in 2021. However, infections and diseases pose a significant challenge to aquaculture, leading to the loss of millions of farmed fish annually.
Researchers have now introduced a novel solution to this problem: injecting alligator DNA into farm-raised catfish to enhance their disease resistance.
While this innovation may sound like the premise of a Southern gothic horror thriller, the scientists leading the project assure the public that there is no cause for alarm.
In initial trials, the introduction of alligator genes appeared to increase the catfish’s resistance to infection. In the future, this approach could potentially reduce the environmental impact of fish farming, decrease waste, and make the process more resource-efficient. Importantly, experts suggest that diners are unlikely to notice any difference when consuming genetically modified catfish.
“I would eat it in a heartbeat,” says Rex Dunham, an aquaculture scientist at Auburn University, who contributed to the project.
Although their work has yet to undergo peer review, the scientists have published a paper detailing their findings on the preprint server bioRxiv.
Alligators possess a gene responsible for producing an antimicrobial protein known as cathelicidin. This protein helps prevent infections in wounds sustained by alligators during combat.
The researchers hypothesized that this same gene could enhance catfish’s ability to resist diseases. To test their theory, they used the CRISPR gene-editing tool to insert the alligator gene containing the blueprint for cathelicidin into the genomes of catfish.
To prevent the genetically modified catfish from reproducing, which could have ecological consequences if released into the wild, the researchers strategically injected the alligator gene into the part of the catfish genome regulating a hormone necessary for spawning.
In experiments assessing disease resistance, the genetically modified catfish demonstrated survival rates two to five times higher than their unedited counterparts when exposed to two types of bacteria known to cause infections.
However, gene editing is a complex and challenging process, and repeating it for each new generation of fish may be necessary. Furthermore, gaining approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the consumption of genetically modified catfish will require a lengthy and rigorous process. Convincing consumers to embrace transgenic fish may also prove to be a challenge.
Despite these obstacles, experts see promise in this concept. While it remains uncertain whether genetically modified catfish will find their way to dinner plates, this research represents a “breakthrough in aquaculture genetics,” according to the scientists. Last year, Auburn researchers also mapped the genome of the blue catfish for the first time.
Beyond catfish, gene-editing technologies have been applied to improve various areas, including agriculture, disease treatment, and cancer research, though they remain the subject of ethical and regulatory discussions.